In my previous article I describe the role of the Solution Architect within the TOGAF ADM, mostly acting between phases E to G, with a specific focus on E (Opportunities and Solutions) and F (Migration Planning). This article will cover the role in phase G: Implementation governance.
The objective of that phase is to formulate recommendations for each implementation project, and govern and manage an architecture contract covering the overall system implementation and deployment. In companies where the maturity is high, it would be perfectly acceptable to have the Solution Architect acting in the name of the Enterprise Architecture team and coordinate activities during the phase G.
TOGAF defines objectives during that phase and each of them may be detailed as follows.
► To formulate recommendations for each implementation project (Source: TOGAF 9)
The Solution Architect with the Enterprise Architecture team and the Development Team:
- Participates in assessment of solutions needs consistent with the global business strategies
- Re-analyzes business practices.
- Provides business analysis and documents process design of system functions and processes as identified in the phase B.
- Recommends application design within the development team. Supervises and ensures quality delivery of the analysis, design, and build of the hardware, network, and common software platform components of software releases with the development team.
- Assesses identified technologies from the phase D, and makes sure that solution options are based on the target architecture. Note: He will be directly accountable for the acceptance of technology architecture deliverables by the client.
- Participates in the planning, development, maintenance, installation, configuration, documentation, training and implementation of new applications/solutions. He is accountable for the documenting requirements (hardware, network, and configuration) captured during the previous ADM phases. He may also develop the engineering documentation.
- Participates in the development of functional specifications for developers related to modifying functionality, report development, outputs and interfaces.
- Works with internal customers, external consultants, IT staff and other stakeholders to refine requirements when needed.
- Leads and participates in developing and facilitating end user workshops for the solution.
- Supports existing applications within the company’s active portfolio and extends their use where appropriate according to the gap analysis.
- Coordinates and/or participates in the planning and execution of application testing.
► To govern and manage an Architecture Contract covering the overall implementation and deployment process (Source: TOGAF 9)
He identifies if there are any issues between the architecture and the implementation organization.
► To perform appropriate governance functions while the solution is being implemented and deployed (Source: TOGAF 9)
He will refer to existing governance best practices such as IT Service Management, Project Management, Risk Management, Security Management, and Audit management (for example).
► To ensure conformance with the defined architecture by implementation projects and other projects (Source: TOGAF 9)
He will Review ongoing implementation governance and architecture compliance for each building block.
► To ensure that the program of solutions is deployed successfully, as a planned program of work (Source: TOGAF 9)
He will Review ongoing implementation governance and architecture compliance for each building block.
► To ensure conformance of the deployed solution with the Target Architecture (Source: TOGAF 9)
He will support the architecture design review using a customized checklist as defined in TOGAF.
► To mobilize supporting operations that will underpin the future working lifetime of the deployed solution (Source: TOGAF 9)
The Solution Architect with the Enterprise Architecture team and the IT Operation Team:
- Helps to monitor and supports the operations architecture of for hardware, network, and common software platforms (including configuration approach, deployment, approach, and monitoring approach).
- Supports all hardware, network, and common software platforms in Development, Production, and Operations environments. Must be aware of the status of the system in all environments, and must communicate and manage environment related risks and activities.
- Supports build team by managing configuration of hardware, network, and common software platforms (like Application Servers).
- Establishes and maintains relationship with key clients with-in client IT organization.
- Develops and implements plan for increasing level of technical architecture skill in program staff.
- Ensures consistent implementation of technical components across release activities with the IT Service Management team if it exists (e.g. release manager).
- Identifies production infrastructure related issues in the production environment with the help of both the Service Desk and the System Management team if they exist. Creates and implements issue resolution plans that have to be escalated to the Enterprise Architecture team.
This diagram is a high level representation of the Solution Architect’s activities interacting with all parties involved in the architecture development and delivery.
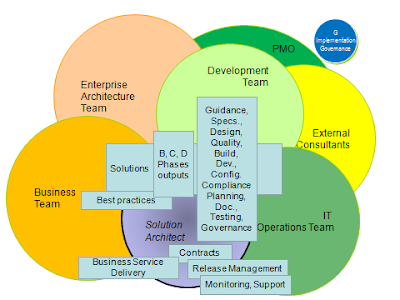
This approach where many activities are led by a designated Solution Architect. The alternative being to share the role between several architects from the Enterprise Architecture team.
